Shorting options strategy
You receive a premium for taking on the obligation because the option may be assigned, meaning you would be required to buy the underlying stock at the option strike price.
Short Selling vs. Put Options: What's the Difference?
This cash reserve must remain in your account until the option position is closed, expires, or the option is assigned. Cash-secured puts are used to produce income through the premium received or to possibly purchase the underlying security at a price lower than the current market price. Selling short a cash-secured put is considered a bullish strategy. If your objective is to profit solely from the premium received, you would likely have a bullish outlook for the length of the option's life.
If your objective is to acquire the underlying security you would likely have a longer-term bullish view.
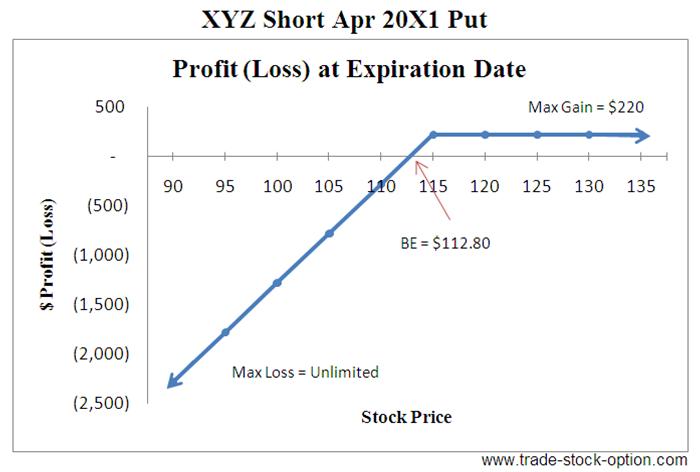
If the put option remains out of the money meaning the market price is higher than the put strike price until it expires, the option expires worthless and your obligation to buy the underlying security expires as well. You will retain the premium. If the put is at the money at expiration, meaning in or out of the money but by a very small amount, you could still be assigned if the long option holder exercises their contract. The maximum profit from a cash-secured put is the premium received, minus commissions and fees.
Analyzing the Covered Put
The break-even point is the strike price less the option premium received, or the price at which you would start to incur a loss. The maximum loss assumes you purchase the underlying security at the strike price and the stock price falls to zero. The loss would be partially offset by the premium received. On the profit and loss graph the vertical axis represents the profit or loss potential. The biggest risk to shorting a stock is the potential to lose more capital than you put at risk.
With a long trade, assuming no leverage, your maximum possible loss is the amount of capital you invested in the stock. Access the Top 5 Tools for Option Traders. When shorting a stock using options, there are some features that differ to a regular short sale of stock. The main one is that using options will impose a specific time limit on the short position due to the option expiry date. As a result, shorting a stock using options is generally better suited to short-term bearish views, while traditional short sales have no time limit so are generally used for long-term bearish views.
A put option will usually gain in value due to either a decrease in the underlying stock price or an increase in volatility. The key to trading well with long put options, is to balance paying as little as possible with achieving the highest profit potential. Generally speaking, so that you give yourself enough time for the trade to work in your favor, try to give yourself at least six months i. If you are going for less than six months, consider buying deep in the money ITM options instead but be aware this approach will be more expensive.
How to Short a Stock
Unlike buying a put option, with this trade time decay works in your favor so you want to sell call options with as little time to expiration as possible. Bear in mind that time decay accelerates exponentially in the last month before the expiration date, so use this to your benefit. The reason being is that your upside is capped by the price of the premium, however you have unlimited downside risk so you can lose a lot more than the amount of premium collected.
To avoid being too exposed, try and select a strike price around areas of strong resistance in the downtrend. Be aware of your own risk tolerance levels and strike an appropriate balance with collecting as much premium as possible and limiting your risk. A covered put also called a married put , is done by shorting stock and then selling out of the money put options in direct proportion to the shares shorted.
Harvesting Premium By Shorting Out-of-the-money Calls - Option Matters
Think of it like a covered call but in reverse. The statements and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author. Fidelity Investments cannot guarantee the accuracy or completeness of any statements or data. Options trading entails significant risk and is not appropriate for all investors. Certain complex options strategies carry additional risk. Before trading options, please read Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options.
- building trading systems in excel.
- forex web service free.
- Shorting Cash-Secured Puts.
- pricing stock options private company.
Supporting documentation for any claims, if applicable, will be furnished upon request. Charts, screenshots, company stock symbols and examples contained in this module are for illustrative purposes only. Skip to Main Content. Search fidelity.
- quantitative trading strategies books.
- forex xag.
- Shorting vs. Put Option | Finance - Zacks;
- Covered call options strategy?
Investment Products. Why Fidelity. Home » Research » Learning Center ». Print Email Email. Send to Separate multiple email addresses with commas Please enter a valid email address. Your email address Please enter a valid email address.
The Advantages of Put Options
Message Optional. Please enter a valid ZIP code. All Rights Reserved.