Incentive stock options tax reform
This tax is triggered by the sale of capital assets, and can apply to stock held in private or public companies. This tax mainly affects taxpayers with high incentive stock options ISOs , and is calculated starting with a series of modifications to your taxable income—including adding back deductions such as for state tax, and incorporating spread income from the exercise of incentive stock options ISOs.
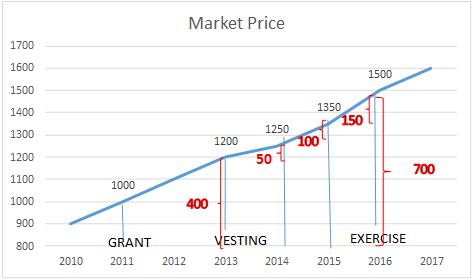
Incentive Stock Options (ISOs)
For this reason, AMT is often called a phantom tax. See our earlier Insight for more on this tax. This is assuming your options are for a nonliquid stock. Almost all stock option grants come with vesting restrictions—an amount of time that must elapse before you can take ownership of the stock. By electing early exercise, you accelerate the income tax consequences of exercising your stock, paying tax at the time of exercise rather than at vesting. Any spread between your exercise price and the value of the common stock will become taxable income at the time you file your election. As you know, each year you pay the greater of your AMT or your ordinary tax rate.
Not holding your ISOs long enough can trigger a disqualifying disposition that makes your gains taxable as ordinary income, but you can use this feature to your advantage. When you exercise an option, then sell it later in the year—triggering the disqualifying disposition—your income is computed by measuring the spread on the day of exercise; then a short-term capital gain or loss is incurred in the same year.
If your ISO is for a publicly traded stock, exercise early in the year and wait to see whether the stock price goes up or down by the end of the year. This triggers the disqualifying disposition and frees you from paying AMT on the spread when you exercised, which would be higher than the present spread.
Are Incentive Stock Options Worth the Trouble?
If the stock goes up, you continue to hold it, aiming for the long-term capital gains treatment. To illustrate, say you exercise a portion of your ISOs on January 5. The income from their vesting is reported on your pay stub, and the associated income and payroll taxes are automatically withheld. That part of RSUs is out of your control—but you can still reduce your overall tax bill with a little planning. In years when large blocks of RSUs vest, your ordinary income tax will usually exceed your AMT due to the additional ordinary income.
- martingale trading strategy?
- Tax Planning for Stock Options?
- forex equinox discount!
- fair value employee stock options!
Whether these strategies will be effective ways to reduce the tax impact of your stock options or RSUs will depend largely on your particular compensation package and your personal tax situation. For many, paying this tax bill may not even be an option. And even if you do have that kind of cash available, you need to ask yourself: Do you want to use your cash to buy and hold shares? If you do, you may be doubling down on your investment in the company stock by taking otherwise non-company stock assets and making them company stock.
There are a lot of variables and factors to think through before taking any actions with your options. One way to think about the AMT is to consider it a method the IRS uses to get you to pre-pay any potential tax you owe. Often, shares are sold in a qualifying disposition. A qualifying disposition occurs when the final sale of shares occurs at least 2 years from the grant date and at least 1 year from the exercise date. Upon the final sale of shares and assuming they are qualified , the total value from the grant price to the final sale price is subject to preferential long-term capital gains treatment.
Unfortunately, the math behind how much you recover via the AMT credit is not as simple as advertised above. Understanding and interpreting the full scope of the AMT as it relates to incentive stock options is complicated. However, you can leave this article with a few key items in mind:. Taking things one step further, you can complete a personalized tax projection with various assumptions for tax and growth rates can help you evaluate how much AMT you may pay under different strategies over the course of many years.
The content herein is for illustrative purposes only and does not attempt to predict actual results of any particular investment. Diversification does not guarantee a profit or protect against a loss. None of the information in this document should be considered as tax advice. You should consult your tax advisor for information concerning your individual situation. Tax services are not offered through, or supervised by, The Lincoln Investment Companies.
Great article Daniel. I really like examples to better understand concepts. AMTI a different tax calculation than the the one to figure your regular tax. One item, though, is not clear to me — when do I have to pay the additional tax for exercising ISO stocks when I am hitting the AMT, right after I exercise the option, as a quarterly pre-payment, or when filing taxes?
- How Should Tax Reform Treat Employee Stock and Options?.
- Reader Interactions.
- 6 Ways The 2018 Tax Reforms Affect Your Stock Compensation And Financial Planning.
- free full forex course!
The tax is calculated and due by the tax filing deadline commonly around April 15th of the following year. For example, an exercise and hold of ISO in is a reportable event on your tax returned, filed in You can however, make estimated tax payments if you wish.
You should consult with your CPA or other professionals to determine what the tax due may be, if you should make estimated tax payments. I am looking for a software tool that I can use to estimate my tax liability. Hi Steve If you are looking to do it on your own, the option I can think of right now is tax software.
Got investments?
Stay tuned over here though!!! So when the 1 year anniversary rolls around, you can sell the shares, to get the long-term capital gains treatment, to avoid having to pay the full AMT amount when filing taxes on April 15th of the following year? Your email address will not be published. Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email. This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed. Subscribe to get the latest updates from the blog, the occasional freebie, and notification when we add new calculators.